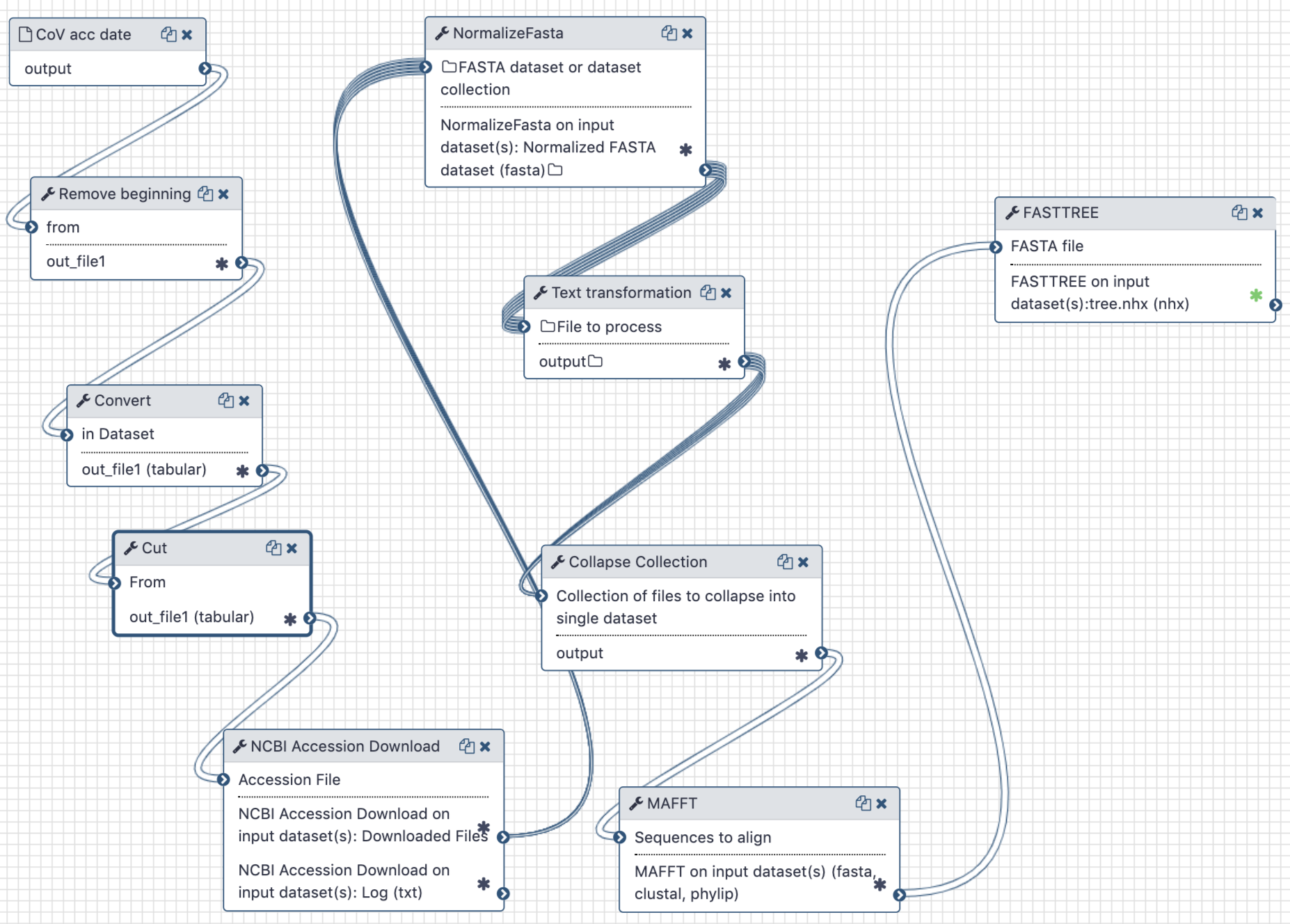
Workflow Type: Galaxy
Open
Stable
Alignment, assembly and annotation of generated transcripts from RNASEQ reads.
Inputs
| ID | Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| List of Illumina accessions | List of Illumina accessions | n/a |
|
| Reference annotation | Reference annotation | n/a |
|
| Reference genome. | Reference genome. | n/a |
|
| SARS-CoV-2 proteins | SARS-CoV-2 proteins | n/a |
|
Steps
| ID | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | UniProt | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/galaxyp/uniprotxml_downloader/uniprotxml_downloader/2.1.0 |
| 5 | Illumina data | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/sra_tools/fasterq_dump/2.10.4 |
| 6 | NCBI BLAST+ makeblastdb | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_makeblastdb/0.3.3 |
| 7 | NCBI BLAST+ makeblastdb | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_makeblastdb/0.3.3 |
| 8 | fastp: Trimmed Illumina Reads | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/fastp/fastp/0.19.5+galaxy1 |
| 9 | Map with BWA-MEM | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/bwa/bwa_mem/0.7.17.1 |
| 10 | MultiQC | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/multiqc/multiqc/1.7 |
| 11 | Filter SAM or BAM, output SAM or BAM | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/samtool_filter2/samtool_filter2/1.8+galaxy1 |
| 12 | Illumina filtered reads | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/samtools_fastx/samtools_fastx/1.9+galaxy1 |
| 13 | TopHat | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/tophat2/tophat2/2.1.1 |
| 14 | Cufflinks | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/cufflinks/cufflinks/2.2.1.2 |
| 15 | Cuffmerge | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/cuffmerge/cuffmerge/2.2.1.1 |
| 16 | Cuffquant | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/cuffquant/cuffquant/2.2.1.1 |
| 17 | Cuffdiff | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/cuffdiff/cuffdiff/2.2.1.5 |
| 18 | gffread | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/gffread/gffread/2.2.1.2 |
| 19 | TransDecoder | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/transdecoder/transdecoder/3.0.1 |
| 20 | Antismash | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/bgruening/antismash/antismash/4.1 |
| 21 | Glimmer ICM builder | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/bgruening/glimmer3/glimmer_build-icm/0.2 |
| 22 | NCBI BLAST+ makeblastdb | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_makeblastdb/0.3.3 |
| 23 | NCBI BLAST+ blastp | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_blastp_wrapper/0.3.3 |
| 24 | NCBI BLAST+ blastp | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_blastp_wrapper/0.3.3 |
| 25 | jackhmmer | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/iuc/hmmer3/hmmer_jackhmmer/0.1.0 |
| 26 | Glimmer3 | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/bgruening/glimmer3/glimmer_knowlegde-based/0.2 |
| 27 | NCBI BLAST+ blastp | toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/repos/devteam/ncbi_blast_plus/ncbi_blastp_wrapper/0.3.3 |
Outputs
| ID | Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| _anonymous_output_4 | _anonymous_output_4 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_6 | _anonymous_output_6 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_7 | _anonymous_output_7 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_8 | _anonymous_output_8 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_9 | _anonymous_output_9 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_10 | _anonymous_output_10 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_11 | _anonymous_output_11 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_12 | _anonymous_output_12 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_13 | _anonymous_output_13 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_14 | _anonymous_output_14 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_15 | _anonymous_output_15 | n/a |
|
| fastq | fastq | n/a |
|
| fast | fast | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_16 | _anonymous_output_16 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_17 | _anonymous_output_17 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_18 | _anonymous_output_18 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_19 | _anonymous_output_19 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_20 | _anonymous_output_20 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_21 | _anonymous_output_21 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_22 | _anonymous_output_22 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_23 | _anonymous_output_23 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_24 | _anonymous_output_24 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_25 | _anonymous_output_25 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_26 | _anonymous_output_26 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_27 | _anonymous_output_27 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_28 | _anonymous_output_28 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_29 | _anonymous_output_29 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_30 | _anonymous_output_30 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_31 | _anonymous_output_31 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_32 | _anonymous_output_32 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_33 | _anonymous_output_33 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_34 | _anonymous_output_34 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_35 | _anonymous_output_35 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_36 | _anonymous_output_36 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_37 | _anonymous_output_37 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_38 | _anonymous_output_38 | n/a |
|
| fasta | fasta | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_39 | _anonymous_output_39 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_40 | _anonymous_output_40 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_41 | _anonymous_output_41 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_42 | _anonymous_output_42 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_43 | _anonymous_output_43 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_44 | _anonymous_output_44 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_45 | _anonymous_output_45 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_46 | _anonymous_output_46 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_47 | _anonymous_output_47 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_48 | _anonymous_output_48 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_49 | _anonymous_output_49 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_50 | _anonymous_output_50 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_51 | _anonymous_output_51 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_52 | _anonymous_output_52 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_53 | _anonymous_output_53 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_54 | _anonymous_output_54 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_55 | _anonymous_output_55 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_56 | _anonymous_output_56 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_57 | _anonymous_output_57 | n/a |
|
| _anonymous_output_58 | _anonymous_output_58 | n/a |
|
Version History
Version 1 (earliest) Created 18th Jun 2020 at 00:17 by Ambarish Kumar
Added/updated 2 files
Open
 master
master7e5d993
 Creators and Submitter
Creators and SubmitterCreators
Not specifiedSubmitter
Tools
License
Activity
Views: 5559 Downloads: 1024 Runs: 5
Created: 18th Jun 2020 at 00:17
Last updated: 1st Jul 2020 at 09:55
 Attributions
AttributionsNone
 Visit source
Visit source Run on Galaxy
Run on Galaxy